Euler :
Pre requisites :
Co-prime definition : Co-prime simply means when HCF of given numbers is 1, i.e, there is nothing common between them. Eg: (1,2), (3,8), (9,19), (4,6,9) etc are co-prime groups.
Meaning : Euler of a Number,N means the number of co-primes to N below it.
Example : Euler of 10 = Number of co-primes to 10 , from 1 to 10. They are : 1,3,7,9 : 4. Hence the Euler of 10 is 4.
Importance : Euler is very important theorem to find Remainders, basically asked in CAT Mocks. Euler is special in a way that, it defines the cyclicity of a number.
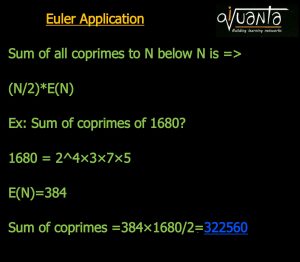
Formula : Now what if the Euler of 100 or 1000, or a big number is asked, counting manually isn’t possible. Hence there is a direct formula to find Euler of any number N.
Let’s say N = a^x*b^y*c^z, where a,b,c are primes.
E(N) = N[(1-1/a)(1-1/b)(1-1/c)]
Example : Euler of 100, (100=2^2*5^2) : E(100) = 100(1-1/2)(1-1/5) = 100(1/2)(4/5) = 40.
It simply means there are 40 co-prime numbers to 100, below 100.
For a prime number P, as p is the only prime so, E(P) = P(1-1/P) = P-1 always.
Application : 1) Ps : Mod just means remainder. So 6 mod 4 =2 or 12 mod 4=0. 
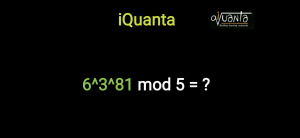
Application: 2)
Application: 3)
Practice Conceptual Questions Now:
(To know it’s answers and solutions, post in iQuanta Facebook group
Tip: All concepts may or may not be applicable, unlike other materials. Play smart, like an entrepreneur.